Mailgun is a popular email relay service to help ensure your emails are delivered to your recipients. In this article we will explain how to configure Mailgun and the Mailgun WordPress plugin to help improve email deliverability.
Step 1: Sign up for Mailgun account
The first step to configuring Mailgun is to sign up for an account. Mailgun is free for the first 10,000 emails every month, making it a great cost-friendly option for websites that don’t send a massive amount of email.
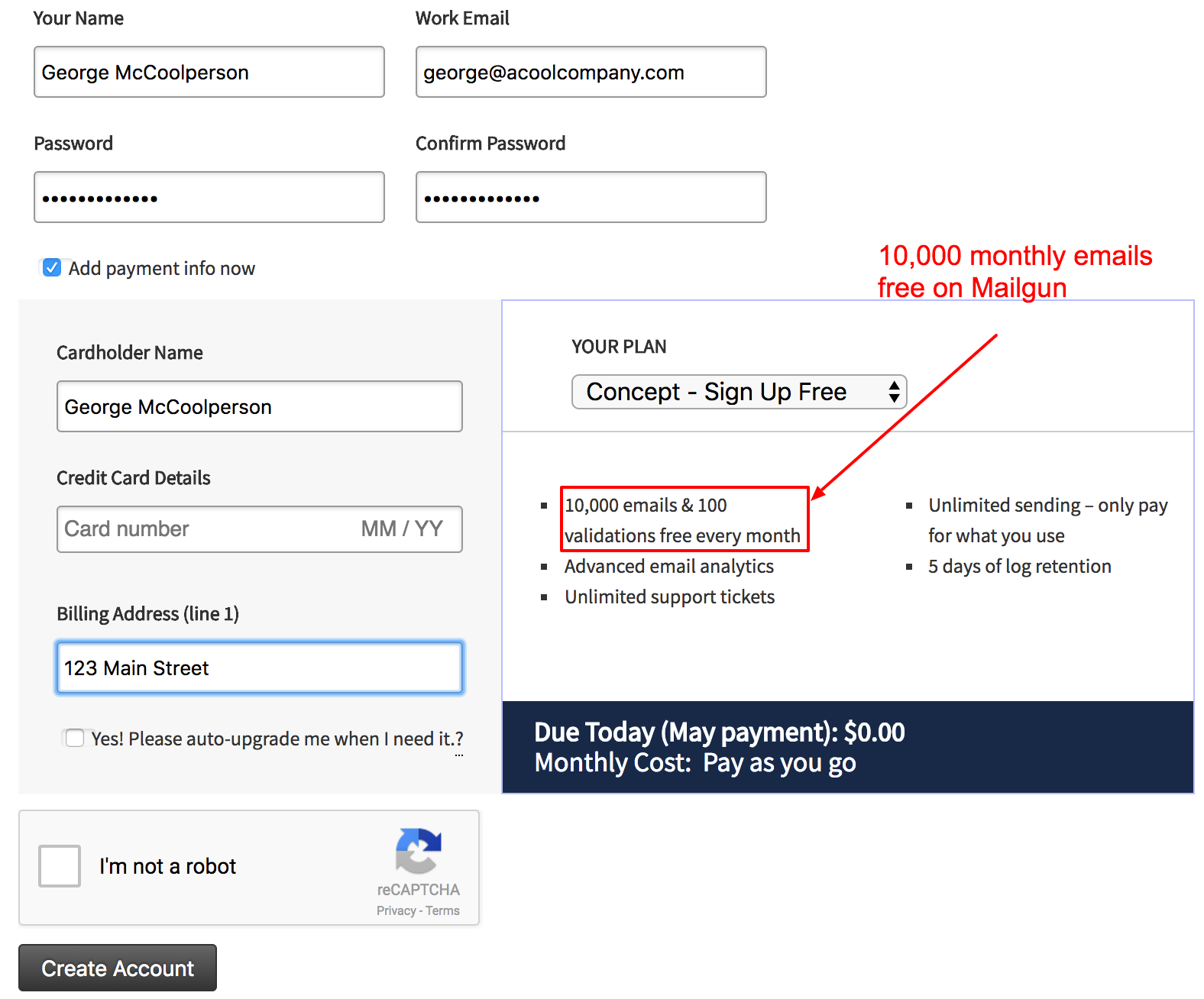
After signing up you will be prompted to verify your account via email and text message. When your account is verified, you will be able to add your domain to Mailgun.
Step 2: Add a Domain
In this step you will need to choose a domain (or subdomain, preferably) for sending mail through your website. In my example I chose the “mail” subdomain of my own domain (mail.areallycoolwebsite.club). Mailgun will then guide you in what records to add to your DNS manager to successfully configure email.
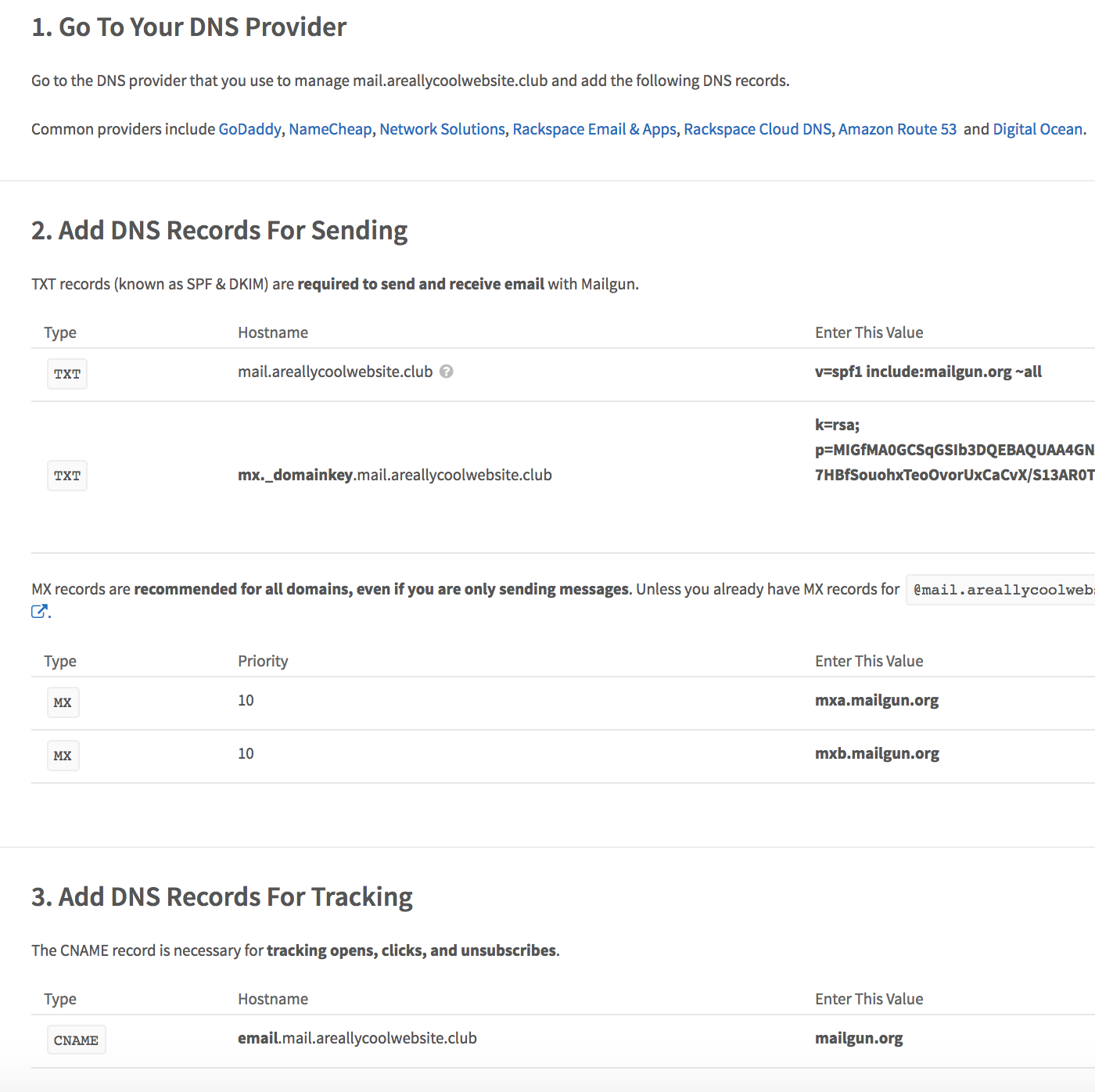
Step 3: Add & Verify DNS Records
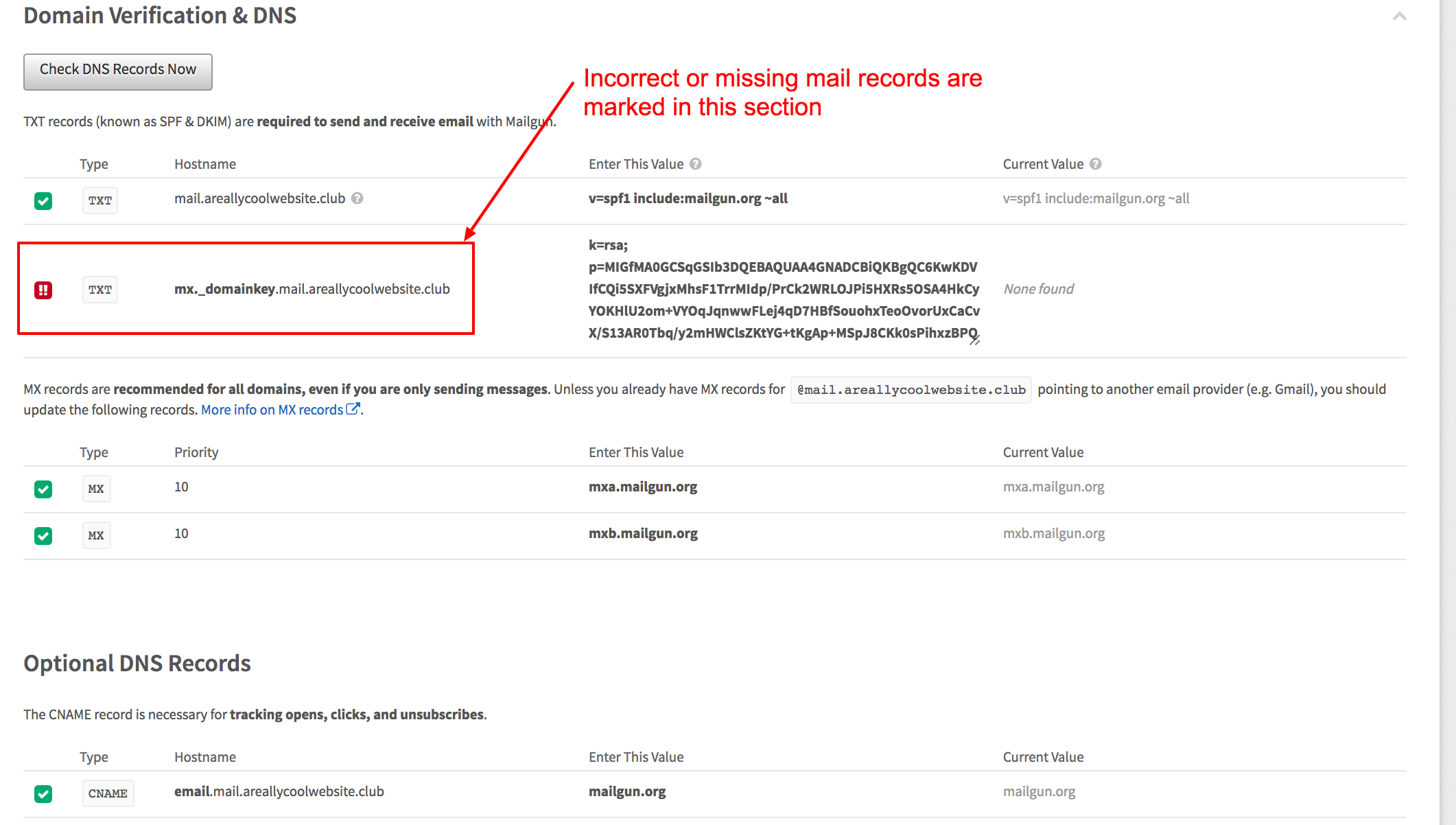
Now you will need to add the records listed on Mailgun’s configuration page in your DNS provider’s dashboard. I manage this domain through Namecheap, and this is where I added the mail records as prompted by Mailgun.
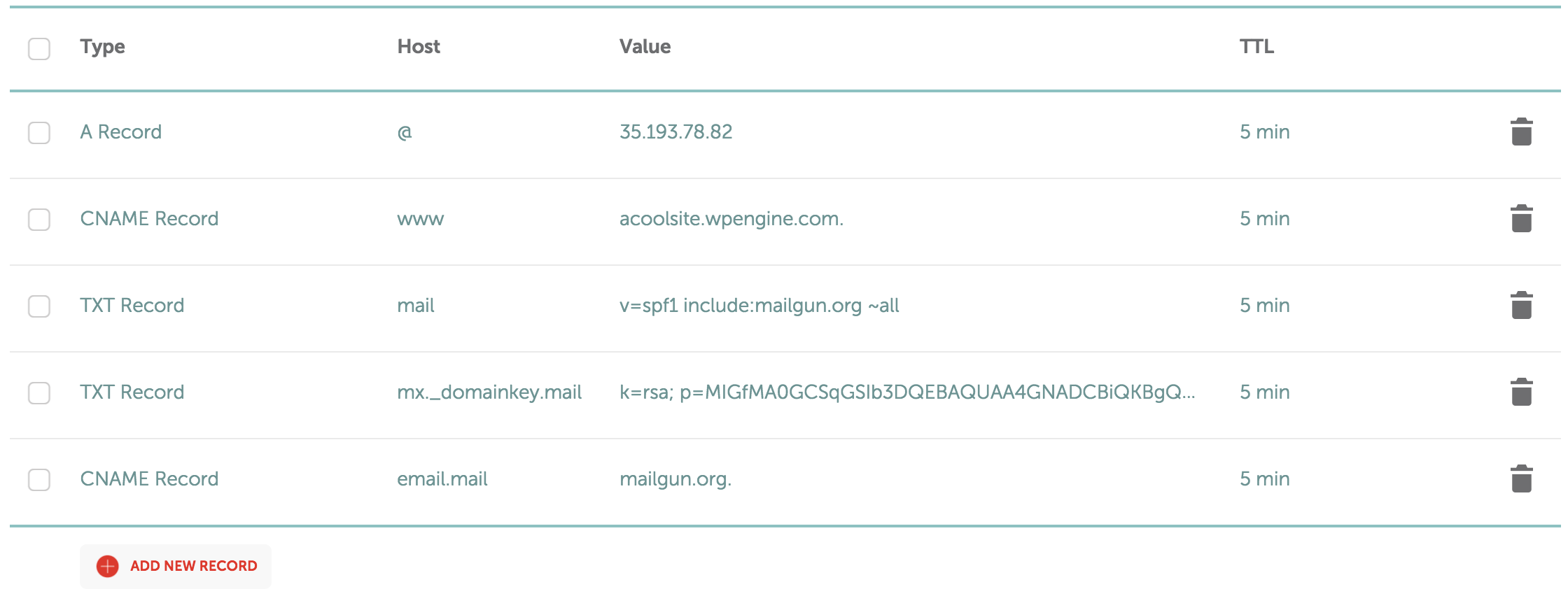

Once your records have been added, you can verify your records have been successfully configured on the Mailgun Domains page. Scroll down and click “Domain Verification & DNS” to check whether your records were successfully configured (remember: these records can take up to 24 hours to propagate).
Step 4: Install & Activate Mailgun Plugin
You will need to login to your WordPress Admin Dashboard for the following steps. Login to your website at the /wp-admin path to access the WordPress Admin Dashboard. Navigate to Plugins > Add New and type “Mailgun” to locate the Mailgun for WordPress plugin. You will be able to recognize it because it is both named “Mailgun” and made by “Mailgun” as the author.
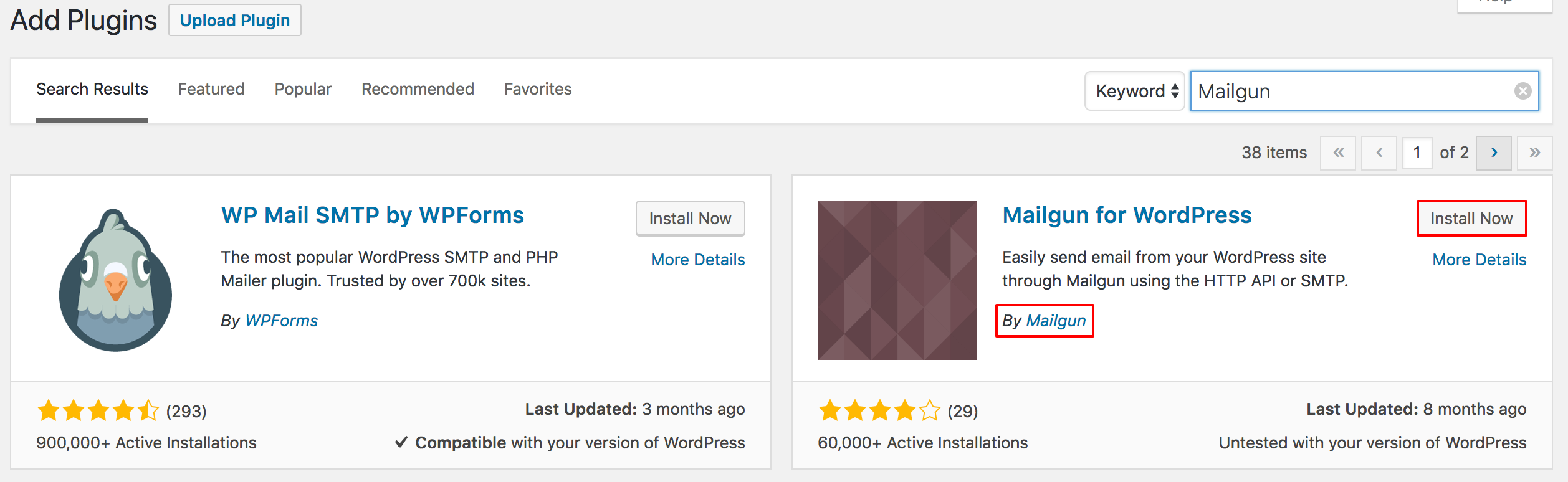
Once it is installed, activate the plugin on the same screen. Then you can configure Mailgun from the Settings > Mailgun section.
Step 5: Configure Mailgun Plugin
Once you have arrived to the Settings page, you will enter some important settings from the Mailgun portal. Firstly, ensure “Yes” is selected for the Use HTTP API setting. This ensures your mail will be relayed over the Mailgun API instead of using an SMTP port. The API setting is more reliable, and works even when normal mail ports are closed.
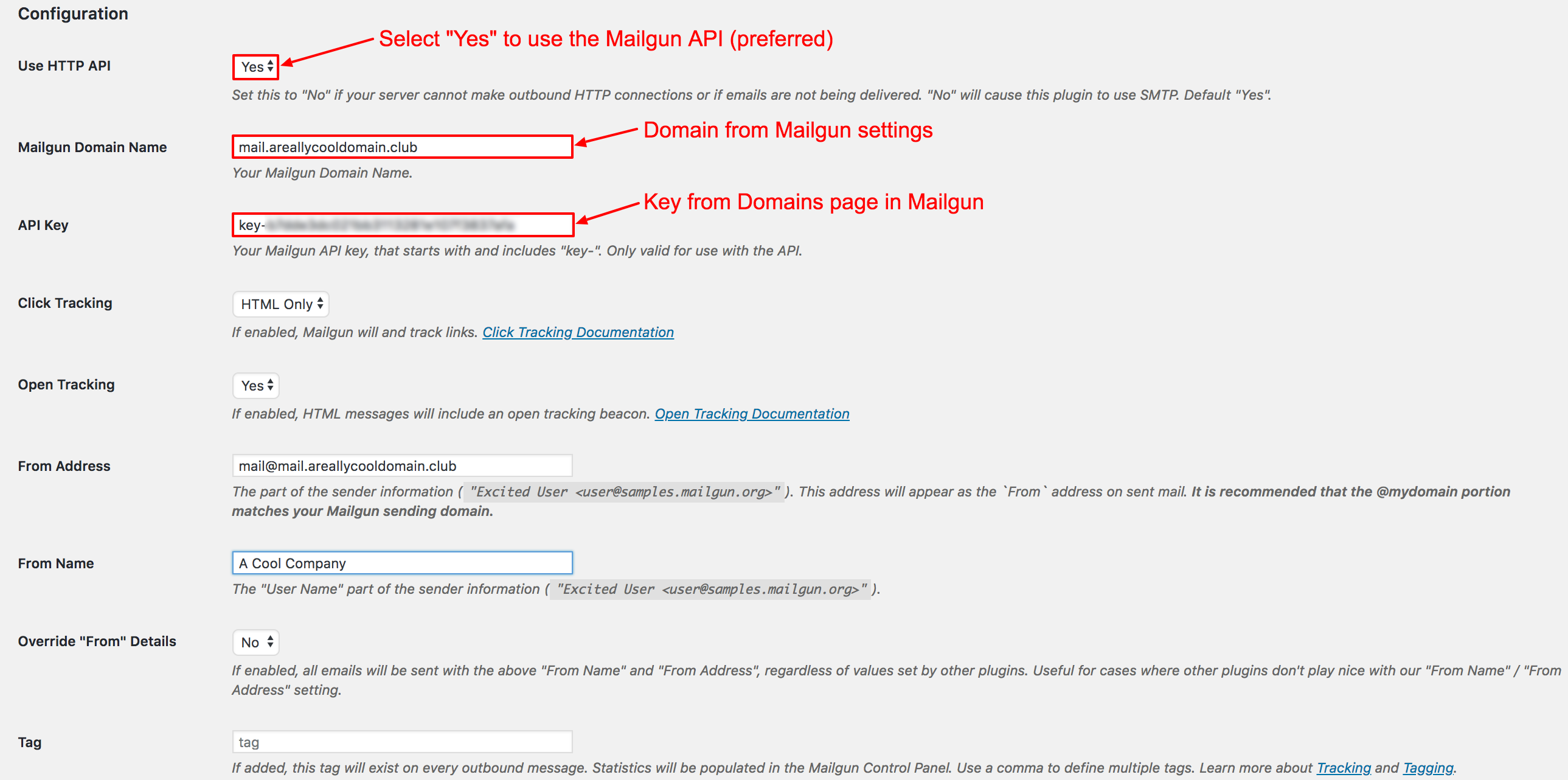
Then, enter the domain you configured for use with Mailgun in the Mailgun Domain Name field. Enter the API Key from the Mailgun Domains page, then continue to set the rest of your preferences before saving. After saving you will be able to send a test email to ensure your settings were configured properly.
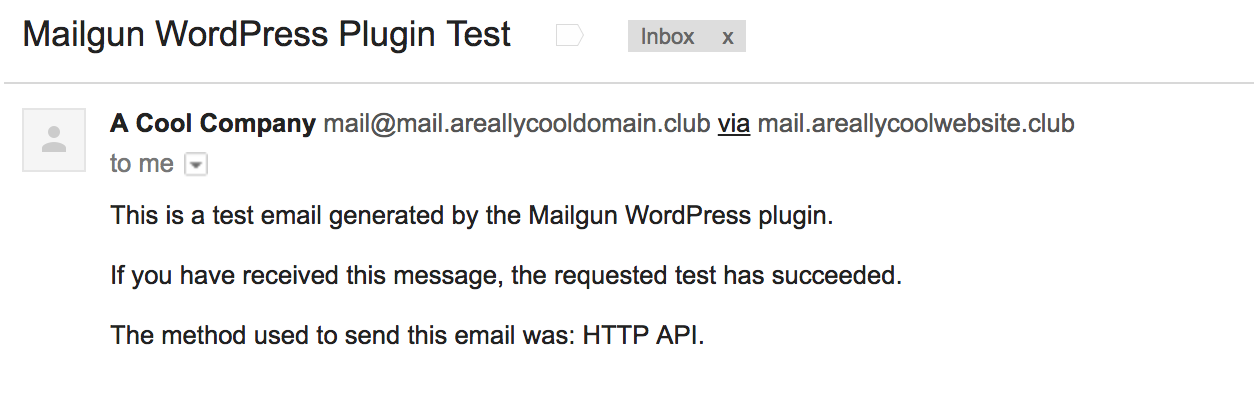
If you encounter any errors, it could mean your DNS settings are still propagating, or that your settings are misconfigured–make sure your Mailgun domain also shows “Active.” If the email is sent successfully, you should receive an email with the following text:
This is a test email generated by the Mailgun WordPress plugin. If you have received this message, the requested test has succeeded. The method used to send this email was: HTTP API.
Step 6: Sending emails through WordPress
Now that your Mailgun settings are configured and tested, your WordPress emails (like password resets, etc.) are automatically sent through Mailgun. You can now add other plugins that will send email through WordPress, like Contact Form 7 or Gravity Forms, to allow your users to send inquiries to you. You may also send newsletters or other mass communications to your users. But remember, your account is free up to 10,000 emails. Beyond that, you can pay for what you use according to Mailgun pricing per plan.
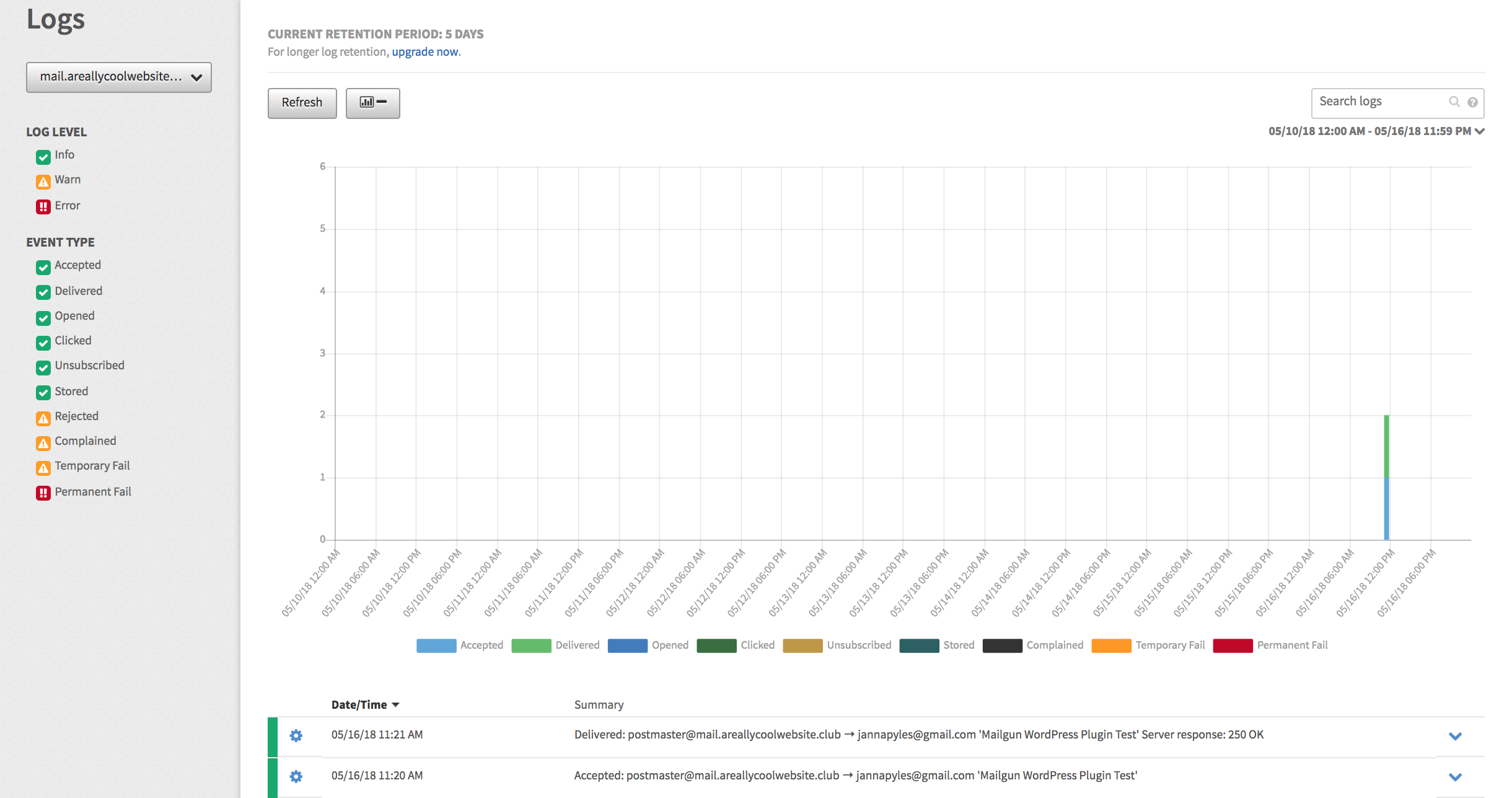
You can track your email deliverability, as well as statistics (accepted, delivered, bounced, opened, clicked, etc) from the Mailgun Logs area.